Подробно ръководство как се работи с еър фрайър Филипс. Въведение в света на еър фрайърите Philips
Еър фрайърите Philips представляват революция в начина, по който приготвяме храната си в домашни условия. Използвайки иновативната технология Rapid Air, тези уреди позволяват да се насладите на хрупкава храна отвън и крехка отвътре с минимално количество или напълно без олио. Това не е просто поредният кухненски уред, а истински помощник за здравословно готвене, който ви помага да намалите консумацията на мазнини с до 80% в сравнение с традиционното пържене.
Всеки модел еър фрайър Philips разполага със система от кошница и тава за готвене, дигитални или ръчни контроли и различни предварително зададени програми в зависимост от модела. Технологията Rapid Air създава мощен вихър от горещ въздух, който обгръща храната и я готви равномерно от всички страни, без да е необходимо да я обръщате постоянно.
Мерки за безопасност преди първа употреба
Преди да започнете да използвате вашия Philips еър фрайър, задължително спазвайте следните мерки за безопасност:
- Отстранете всички опаковъчни материали и промоционални стикери от уреда
- Поставете уреда върху стабилна, хоризонтална, равна и топлоустойчива повърхност
- Осигурете добра вентилация около уреда, като избягвате поставянето му близо до стени или под шкафове, които могат да бъдат повредени от парата
- Никога не пълнете тавата с олио, тъй като това създава опасност от пожар
- Винаги поставяйте продуктите в кошницата, за да предотвратите контакт с нагревателните елементи
- Никога не потапяйте уреда във вода и не го изплаквайте под течаща вода
- Уверете се, че напрежението на уреда съответства на локалното мрежово напрежение
Подготовка на еър фрайъра за употреба
Подготовка преди първо използване
- Измийте внимателно подвижните части (кошницата и тавата) с гореща вода, препарат за съдове и неабразивна гъба преди първата употреба
- Избършете вътрешността и външната част на уреда с влажна кърпа
- Поставете еър фрайъра върху стабилна, хоризонтална повърхност с достатъчно разстояние от всички страни
- Включете щепсела в заземен контакт
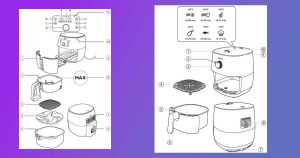
Запознаване с частите на еър фрайъра Филипс
Типичният еър фрайър Philips се състои от:
- Контролен панел (различен според модела, но обикновено включва контроли за температура и време)
- Подвижна кошница за поставяне на храната
- Тава, която държи кошницата
- Отвори за вход и изход на въздуха
- Захранващ кабел
Основна работа с уреда

Вижте и ТОВА: Разлика между мултикукър и фрайър и някои тънкости, които трябва да имате предвид.
Включване на еър фрайъра Филипс
- Поставете вашия Philips еър фрайър върху стабилна, топлоустойчива повърхност
- Включете щепсела в заземен контакт
- Натиснете бутона за вкл./изкл., за да включите уреда
Задаване на температура и време
За дигитални модели (серия HD928X и подобни):
- Натиснете бутона за температура
- Използвайте бутоните за увеличаване или намаляване, за да изберете желаната температура
- Натиснете бутона за време
- Използвайте бутоните за увеличаване или намаляване, за да зададете времето за готвене
- Натиснете бутона Старт/Пауза, за да започнете готвенето
За модели с ръчно управление (HD9217 и подобни):
- Завъртете копчето за контрол на температурата до необходимата температура
- Завъртете копчето на таймера/вкл., за да зададете времето за готвене, което автоматично включва еър фрайъра
Основен процес на готвене
- Издърпайте тавата с кошницата от еър фрайъра, използвайки дръжката
- Поставете продуктите в кошницата, като внимавате да не надвишите индикацията MAX
- Плъзнете тавата обратно във еър фрайъра
- Задайте подходящата температура и време, както е описано по-горе
- Някои продукти изискват разклащане или обръщане по средата на готвенето (направете справка с таблицата за храна в ръководството на вашия конкретен модел)
- За да разклатите продуктите, издърпайте тавата, използвайки дръжката, разклатете я над мивката и я плъзнете обратно в еър фрайъра
- Процесът на готвене автоматично се паузира, когато извадите тавата, и се възобновява, когато я поставите обратно
- Когато таймерът звънне, храната ви е готова
Разширени функции за готвене
Използване на предварително зададени програми за готвене
Много модели еър фрайъри Philips предлагат предварително зададени програми за готвене на често приготвяни храни:
- Включете еър фрайъра, като натиснете бутона за захранване
- Натиснете бутона за предварителна настройка, за да преминете през наличните предварително зададени програми
- След като изберете желаната предварителна настройка, можете да регулирате времето и температурата, ако е необходимо
- Натиснете бутона Старт/Пауза, за да започнете готвенето с избраната предварителна настройка
Режим за поддържане на топлина
Тази функция поддържа храната ви при идеална температура до 30 минути след готвене:
- Натиснете бутона за поддържане на топлина по време на готвене или след като готвенето приключи
- За да излезете от режима за поддържане на топлина, натиснете бутона Старт/Пауза, бутона за поддържане на топлина отново или изключете еър фрайъра
Приготвяне на домашни пържени картофи
Въздушните фритюрници Philips се отличават с готвене на хрупкави домашни пържени картофи с минимално количество олио:
- Обелете и нарежете картофите на пръчици (препоръчителна дебелина: 1/2 x 1/2 инча)
- Накиснете картофените пръчици във вода за поне 30 минути, отцедете ги и ги подсушете с кухненска хартия
- Сипете 1/2 супена лъжица олио в купа, добавете картофените пръчици и разбъркайте, докато се покрият
- Поставете картофите в кошницата на въздушния фритюрник, без да надвишавате линията MAX
- Задайте температура на приблизително 180°C (350°F)
- Гответе за около 20-25 минути (времето варира според модела и количеството)
- Разклатете кошницата по средата на готвенето за равномерни резултати
Интеграция с приложението HomeID (NutriU)

Още нещо интересно ТУК: Вайбър: Инсталиране на телефон Андроид, iPhone и компютър
По-новите модели въздушни фритюрници Philips предлагат WiFi свързаност, за да подобрят вашето готвене чрез приложението HomeID (по-рано известно като NutriU):
Настройка на връзката с приложението HomeID
- Изтеглете приложението Philips HomeID от Google Play Store или Apple App Store
- Създайте акаунт или влезте
- Уверете се, че вашият смартфон е свързан към домашната WiFi мрежа
- Отворете приложението и изберете вашия модел въздушен фритюрник
- Следвайте инструкциите в приложението, за да свържете въздушния фритюрник към WiFi
Функции на приложението HomeID
Приложението HomeID предлага няколко предимства за собствениците на въздушни фритюрници Philips:
- Достъп до обширна библиотека с рецепти за въздушния фритюрник
- Инструкции за готвене стъпка по стъпка
- Възможност за изпращане на настройки за готвене директно към съвместими въздушни фритюрници
- Информация за хранителните стойности на рецептите
- Персонализирани препоръки за рецепти въз основа на предпочитанията
- Интелигентни списъци за пазаруване, генерирани от избраните рецепти
- Известия за готвене, когато ястието ви е готово
Почистване и поддръжка
След всяка употреба
- Изключете въздушния фритюрник и го оставете да се охлади
- Извадете тавата и кошницата от уреда
- Почистете тавата и кошницата с гореща вода, мек препарат за съдове и неабразивна гъба
- Забележка: В повечето модели тези части могат да се мият в съдомиялна машина
- Избършете вътрешността на уреда с влажна кърпа
- Почистете нагревателния елемент с четка за почистване, за да отстраните остатъците от храна, ако е необходимо
Ръководство за почистване на специфични компоненти
- Кошница за храна и тава: Гореща вода, препарат за съдове и неабразивна гъба или съдомиялна машина
- Вътрешност на уреда: Влажна кърпа
- Нагревателен елемент: Четка за почистване (уверете се, че уредът е охладен първо)
- Външна част на уреда: Влажна кърпа
Съхранение
- Изключете уреда и го оставете да се охлади напълно
- Уверете се, че всички части са чисти и сухи преди съхранение
- Поставете кабела в отделението за съхранение на кабела, ако вашият модел има такава функция
- Съхранявайте на чисто, сухо място, далеч от пряка слънчева светлина
Отстраняване на често срещани проблеми
Въздушният фритюрник не се включва
- Проверете дали щепселът е правилно поставен в контакта
- Проверете дали таймерът е правилно настроен (за модели с ръчно копче за таймер)
- Уверете се, че тавата е правилно поставена в уреда
Храната не се готви равномерно
- Определени храни трябва да се разклащат по средата на готвенето
- Съставките, поставени една върху друга, трябва да се разклащат по време на готвене
- Не препълвайте кошницата над индикацията MAX
Бял дим излиза от уреда
- Приготвяте мазни съставки. Изтичането на олио в тавата може да произведе бял дим, което е нормално
- Тавата все още съдържа мазни остатъци от предишна употреба
Домашните пържени картофи не са хрупкави
- Накиснете сурови картофени пръчици във вода за 30 минути, отцедете и подсушете, преди да добавите олио
- Използвайте пресни, нишестени картофи
- Добавете малко повече олио за по-хрупкав резултат
Заключение
Въздушният фритюрник Philips предлага универсален, здравословен метод за готвене, който осигурява вкусни резултати с минимално количество олио. Следвайки това подробно ръководство, ще можете ефективно да работите с вашия еър фрайър Филипс, да се възползвате от различните му функции и да го поддържате правилно за дългосрочна употреба. Не забравяйте винаги да се обръщате към ръководството за потребителя на вашия конкретен модел за подробна информация за вашия конкретен въздушен фритюрник, тъй като функциите и операциите могат да се различават леко между моделите.
За допълнителни рецепти и вдъхновение за готвене, изтеглете приложението HomeID, което предлага стотици рецепти за въздушен фритюрник и персонализирани препоръки, за да ви помогне да извлечете максимума от вашия Philips еър фрайър.
Непременно вижте и ТОВА: Мнения: Най-добър еър фрайър Косори | 10+ идеи

Марта Савова е журналист и писател, специализиран в областите здравеопазване, технологии и наука. С над 20-годишен опит в сферата, тя е публикувала множество изследователски статии и има страст към споделянето на знания. Марта е редовен сътрудник на различни медии.