An Unveiling of Stars: The Expanded Zodiac and the Forgotten Ophiuchus, 13 Sign – Astrology. Chart
The Sun’s Journey: How It Relates to Your Astrological Sign
At the heart of astrology is the Sun’s journey through the different constellations, which directly corresponds to the astrological sign assigned to us at birth. Traditionally, your zodiac sign is determined by which constellation the Sun was ‘in’ on your day of delivery. It is why astrological signs are often called ‘Sun signs.’
To demonstrate how this translates to a 13-sign zodiac system, consider the following table:
| Zodiac Sign | Traditional Dates | 13-Sign Dates |
|---|---|---|
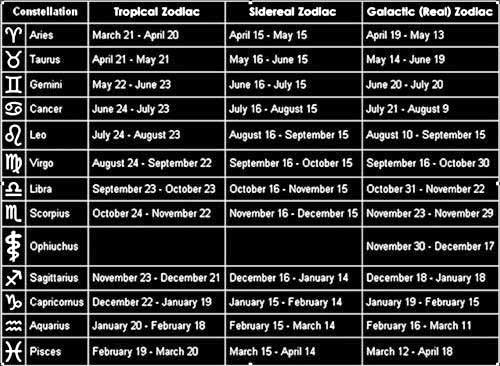
| Aries | March 21 – April 19 | April 19 – May 13 |
| Taurus | April 20 – May 20 | May 14 – June 19 |
| Gemini | May 21 – June 20 | June 20 – July 20 |
| Cancer | June 21 – July 22 | July 21 – August 9 |
| Leo | July 23 – August 22 | August 10 – September 15 |
| Virgo | August 23 – September 22 | September 16 – October 30 |
| Libra | September 23 – October 22 | October 31 – November 22 |
| Scorpio | October 23 – November 21 | November 23 – November 29 |
| Ophiuchus | N/A | November 30 – December 17 |
| Sagittarius | November 22 – December 21 | December 18 – January 18 |
| Capricorn | December 22 – January 19 | January 19 – February 15 |
| Aquarius | January 20 – February 18 | February 16 – March 11 |
| Pisces | February 19 – March 20 | March 12 – April 18 |
This table clearly illustrates that the introduction of the 13th sign, Ophiuchus, significantly alters the dates associated with each astrological sign in the 13-sign system compared to the traditional zodiac.Astrology, an ancient and complex study of the celestial heavens, has been a significant part of human life across different cultures for thousands of years. Despite the evolution of science and technology, the fascination with the cosmos and our placement within it remains unchanged. We are introduced to the world of astrology through the familiar 12-sign Zodiac, a framework that paints the celestial canvas with a broad stroke. Each sign signifies a particular portion of the year, correlated with distinct personality traits, strengths, and weaknesses.
Introduction to the Traditional Zodiac
The traditional Zodiac is a circular belt of the heavens containing our solar system’s path, also known as the ecliptic. This ecliptic is divided into 12 equal parts, each 30 degrees wide, representing the twelve houses of the Zodiac. These houses are occupied by the familiar Zodiac signs: Aries, Taurus, Gemini, Cancer, the strong Leo, Virgo, Libra, the doubtful Scorpio, Sagittarius, Capricorn, Aquarius, and Pisces. Each Zodiac sign corresponds to a period within the year, effectively serving as a celestial map guiding astrologers’ interpretations and predictions.
Contents
- The Unfolding of Cosmic Mystery: Understanding the 13-Sign Astrology Chart
- The Cosmos Expanded: 13-Sign Astrology Deep Dive
- Ophiuchus: The 13th Zodiac Sign
- Astrological Systems: East vs. West
- Astrology in Practice: Understanding Your Real Zodiac Sign
- 13-Sign Astrology and Its Implication on Astrology-Based Solutions
The Forgotten Sign: Ophiuchus
However, amidst this well-recognized wheel of Zodiac signs lies a forgotten 13th sign: Ophiuchus. Known as the „Serpent Bearer,“ this constellation sits on the ecliptic between Scorpius to the west and Sagittarius to the east. According to Greek mythology, Ophiuchus is identified as Asclepius, the renowned healer who was able to raise the dead, thus attracting the wrath of Hades and, subsequently, Zeus’s thunderbolt. But why, one might wonder, is such a constellation with such a compelling mythological narrative omitted from our conventional Zodiac wheel?
Evolution from 12 to 13 sign Astrology
The key to understanding this lies in the evolution from the 12-sign to the 13-sign Zodiac. When the Babylonians, considered the founders of astrology, created their Zodiac around 3000 years ago, they divided the ecliptic into 12 equal parts for calendrical convenience, aligning with their 12-month lunar calendar. However, this meant ignoring the 13th constellation, Ophiuchus, despite its presence on the ecliptic. This decision has resonated throughout centuries, resulting in the Zodiac system we are familiar with today.
But as our understanding of astronomy improved and the precision of celestial measurements increased, the omission of Ophiuchus from the Zodiac became less justifiable. It led to the proposal of a 13-sign Zodiac, an expansion of the traditional Zodiac system to acknowledge the astronomical reality of the ecliptic’s thirteen constellations.
In the following sections, we’ll delve deeper into this 13-sign astrology chart, exploring its significance, implications, and the unique role of Ophiuchus. So, buckle up as we embark on this cosmic journey, revealing the mysteries of the oft-overlooked 13th Zodiac sign, Ophiuchus.
The Unfolding of Cosmic Mystery: Understanding the 13-Sign Astrology Chart
Concept and Origin of the 13-Sign Astrology
To align astrological practices with astronomical facts, we delve into the concept and origin of the 13-sign astrology. To understand this, we must travel back to ancient Babylon. Despite their advanced understanding of celestial movements, the Babylonians, for their ease, conveniently divided the sky into twelve even parts corresponding to their 12-month lunar calendar, bypassing the thirteenth constellation, Ophiuchus.
However, the continued exploration of celestial movements, especially in contemporary times, compelled the astrological community to reconsider the traditional 12-sign system. In the 1970s, a pioneer in this movement, astrologer Walter Berg, proposed a 13-sign astrology system that included Ophiuchus and adjusted the dates of the other signs to match their actual, current positions in the sky. Thus, the journey from a 12-sign to a 13-sign zodiac system wasn’t a result of random chance but rather an endeavor to align astrology more accurately with astronomy.
The Role of Ophiuchus in the Modern Astrological Chart
Including Ophiuchus in the modern astrological chart signifies a shift in astrological thinking. It presents a refreshed perspective on how we perceive our connection with the cosmos and understand ourselves through astrology.
Ophiuchus, often represented by a man wrestling a serpent, echoes themes of struggle, healing, and rebirth—attributes that resonate with the constellation’s mythological backstory. Unlike the other zodiac signs, primarily based on inanimate objects or animals, Ophiuchus symbolizes humanity, representing our constant struggle with life, the pursuit of healing, and resilience.
In the following sections, we will continue to explore the characteristics and implications of each zodiac sign within the 13-sign system, including the mysterious Ophiuchus, providing a comprehensive understanding of this innovative astrological paradigm.
The Cosmos Expanded: 13-Sign Astrology Deep Dive
Analysis of the 13 Signs: Dates, Personality Traits, and Compatibility
A shift from the traditional 12-sign to the 13-sign astrology system impacts the dates corresponding to each sign and provides new insights into personality traits and compatibility. With the inclusion of Ophiuchus, the interpretation of our celestial blueprint becomes more detailed and nuanced. Let’s dive deeper into each of these 13 signs:
NOTE: This is a comprehensive overview. Each sign can be further explored in individual articles or subsections.
| Zodiac Sign | Dates | Personality Traits | Best Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aries | April 19 – May 13 | Passionate, independent, courageous | Leo, Sagittarius |
| Taurus | May 14 – June 19 | Reliable, patient, practical | Virgo, Capricorn |
| Gemini | June 20 – July 20 | Adaptable, outgoing, intelligent | Libra, Aquarius |
| Cancer | July 21 – August 9 | Compassionate, intuitive, loyal | Scorpio, Pisces |
| Leo | August 10 – September 15 | Generous, creative, bold | Aries, Sagittarius |
| Virgo | September 16 – October 30 | Practical, analytical, hardworking | Taurus, Capricorn |
| Libra | October 31 – November 22 | Diplomatic, gracious, fair-minded | Gemini, Aquarius |
| Scorpio | November 23 – November 29 | Brave, passionate, resourceful | Cancer, Pisces |
| Ophiuchus | November 30 – December 17 | Curious, passionate, dedicated | Scorpio, Pisces |
| Sagittarius | December 18 – January 18 | Generous, idealistic, great sense of humor | Aries, Leo |
| Capricorn | January 19 – February 15 | Responsible, disciplined, self-control | Taurus, Virgo |
| Aquarius | February 16 – March 11 | Original, independent, humanitarian | Gemini, Libra |
| Pisces | March 12 – April 18 | Compassionate, intuitive, wise | Cancer, Scorpio |
Special Feature: Ophiuchus – The Serpent Bearer
Taking a closer look at Ophiuchus, the Serpent Bearer, we find that this sign’s traits resonate strongly with its symbol—a figure wrestling with a snake. Those born under Ophiuchus are seen as healers, innovators, and seekers of wisdom and knowledge, reflecting the struggle, healing, and enlightenment aspects of the sign.
Ophiuchus-born are known for their ability to navigate both the physical and metaphysical realms, reflecting a deep sense of curiosity and desire for exploration. This connection with the intangible can make Ophiuchus-born individuals more prone to spiritual pursuits and esoteric knowledge, making them excellent healers, philosophers, and scholars.
Comparison Table: 12-Sign vs 13-Sign Astrology
Understanding the difference between 12-sign and 13-sign astrology can be a challenging task. Therefore, we provide a comparison table to illustrate the fundamental differences:
| 12-Sign Astrology | 13-Sign Astrology | |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Signs | 12 | 13 |
| Sign Dates | Fixed, does not consider precession | Adjusted to the precession of equinoxes |
| Includes Ophiuchus? | No | Yes |
| Basis | Solar calendar, symbolic connections | Sidereal time, astronomical connections |
As we progress further into the world of 13-sign astrology, we’ll examine how this astrological system can provide a more comprehensive understanding of human personality and potential.
Ophiuchus: The 13th Zodiac Sign
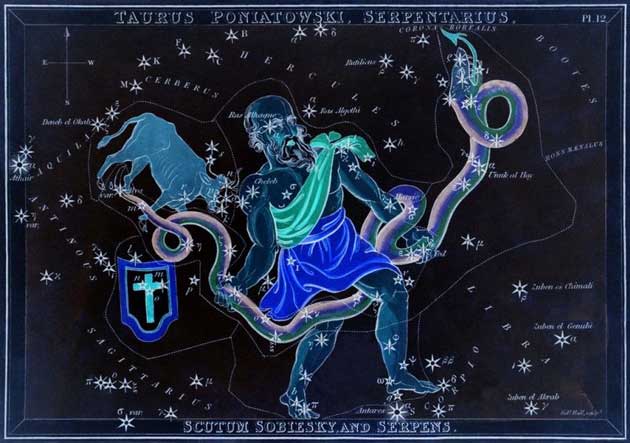
In-Depth Look at Ophiuchus: The Mythology and Astronomy
Dive deep into the constellation of Ophiuchus, the Serpent Bearer, and you will discover a treasure trove of mythology and astronomical knowledge.
In Greek mythology, Ophiuchus is associated with Asclepius, the god of medicine and healing. The son of Apollo, Asclepius, learned the secrets of keeping sudden death at bay after observing one serpent bringing healing herbs to another. However, his skills became so advanced that he could get the dead back to life, a feat that disturbed the natural order and led to his demise at the hands of Zeus. Yet, as a testament to his contributions, Asclepius was placed among the stars in the constellation Ophiuchus.
From an astronomical perspective, Ophiuchus is a large and notable constellation around the celestial equator. It is positioned between Aquila, Serpens, and Hercules, northwest of the Milky Way’s center. The Sun passes directly through Ophiuchus from about November 30 to December 18, which led to its inclusion in the 13-sign zodiac.
Ophiuchus: Characteristics and Personality Traits
As the 13th marvelous sign of the zodiac, Ophiuchus carries some distinct personality traits. These individuals tend to be passionate, curious, and dedicated. Ophiuchus-born are also seekers of wisdom and knowledge, aligning with the sign’s association with Asclepius, the god of medicine and healing. They often have a strong inclination towards pursuits that involve healing or helping others, whether in the medical field, psychology, or social work.
Despite their dedication, Ophiuchus individuals often struggle to balance their personal and professional lives, reflecting the struggle of Asclepius against the natural order. Yet, their strong sense of compassion and wisdom often guides them toward making decisions that benefit the greater good.
Compatibility of Ophiuchus with Other Signs
With its unique characteristics, Ophiuchus has special compatibility with certain signs. Generally, they find their best matches with those who share their passion for exploration and wisdom, typically other water signs like Scorpio and Pisces.
| Ophiuchus Compatibility | Comments |
|---|---|
| High | Scorpio, Pisces |
| Moderate | Cancer, Virgo, Capricorn |
| Low | Aries, Gemini, Leo, Libra, Sagittarius, Aquarius |
Just as the Ophiuchus-born individual is a blend of passion and wisdom, understanding this 13th zodiac sign also requires a blend of astronomical knowledge and astrological interpretation. As we continue to explore the depth of the 13-sign zodiac, we hope this focus on Ophiuchus illuminates some of the intriguing aspects of this fascinating addition to our celestial horoscope.
Astrological Systems: East vs. West

A Brief Introduction to Vedic Astrology
Let’s embark on a journey to the East, where Vedic Astrology, also known as Jyotish, has been integral to Indian spiritual traditions for thousands of years. Named for the Sanskrit word ‘Jyoti,’ which means ‘light,’ Vedic Astrology sheds light on a person’s life path, illuminating the individual’s karmic tendencies and potential outcomes.
Vedic Astrology is mainly based on the sidereal zodiac, where the signs align with their corresponding constellations in the sky. This system is highly predictive and complex, using intricate mathematical calculations based on the precise moment and geographical location of one’s birth. The natal chart in Vedic Astrology, known as the ‘Kundali,’ is a comprehensive map of the heavens at the exact moment of birth, divided into 12 houses and featuring a combination of planets and signs that shape a person’s destiny.
Comparing Western and Vedic Astrology: Key Differences
While Western and Vedic Astrology provides valuable insights, they approach astrological interpretation differently. Western Astrology, as we’ve seen, is based on the tropical zodiac, where the signs are linked to the seasons rather than the constellations. In contrast, Vedic Astrology uses the difficult sidereal zodiac, which aligns more closely with the actual constellations.
Another critical distinction lies in the emphasis each system places on different aspects of life. Western Astrology focuses more on psychological patterns and personality traits, particularly in its modern forms. Vedic Astrology, on the other hand, delves into the karmic tendencies of an individual, predicting major life events and circumstances based on the planetary positions at the time of birth.
| Aspect | Western Astrology | Vedic Astrology |
|---|---|---|
| Zodiac Used | Tropical | Sidereal |
| Focus | Personality traits and psychological patterns | Karmic tendencies and major life events |
Does Vedic Astrology Acknowledge the 13th sign?
Regarding including the 13th sign, Ophiuchus, it’s interesting that Vedic Astrology does not acknowledge this addition. It is largely because Vedic Astrology relies on the fixed sidereal zodiac, divided into 12 equal parts corresponding to the 12 traditional signs. Each of these signs, or ‘Rashis’ in Sanskrit, is associated with a specific constellation. As such, incorporating a 13th sign would disrupt the symmetry of this ancient astrological system.
Nonetheless, the discourse around Ophiuchus offers a valuable opportunity for reflection, encouraging astrologers and enthusiasts alike to delve deeper into the complexities of celestial interpretation. Whether we are navigating the 12-sign tropical zodiac, the 13-sign zodiac, or the intricate realms of Vedic Astrology, each system offers unique insights into our human experience, inviting us to explore our relationship with the cosmos in ever-evolving ways.
Astrology in Practice: Understanding Your Real Zodiac Sign
Breaking Down the Astrological Calendar: How Your Sign Changes
The sky and its celestial bodies bring a certain sense of wonder and curiosity. More so, when we start to explore the realm of Astrology and the influence it may wield on our lives. It’s intriguing to delve into, particularly when considering the astrological calendar’s implications.
Astrology uses the concept of ‘solar’ months, determined by the time the Sun takes to pass through each constellation. In the 12-sign system, these months do not strictly adhere to our standard Gregorian calendar. They generally span from around the 20th or 21st of one month to approximately the exact date of the next.
However, with the incorporation of Ophiuchus into the astrological calendar, this sequence undergoes a slight modification. Adding a new sign means the dates traditionally associated with each sign shift to accommodate this 13th constellation. The extent of this change varies depending on the specific 13-sign system being followed.
The Real Impact of Ophiuchus on Your Horoscope
The introduction of Ophiuchus certainly caused a stir among astrology enthusiasts. It posed questions about the validity of previous horoscopes and made many wonder whether their personality traits, previously attributed to their original signs, had now changed. The reality, however, may not be as dramatic as it seems.
The qualities and characteristics traditionally associated with each sign in the 12-sign system remain essentially the same. Adding Ophiuchus doesn’t change these traits; instead, it provides additional attributes for those born under this new sign.
However, with the date shifts, those who once identified as Sagittarians or Scorpios might fall under the Ophiuchus umbrella. It could mean reevaluating one’s horoscope readings and a fresh look into possible personality traits and compatibilities.
Decoding Ophiuchus: Navigating Your Daily Horoscope
With the spotlight on Ophiuchus, there may be new considerations to consider when reading your daily horoscope. You might find it helpful to reflect upon and identify with traits associated with this constellation, such as a penchant for wisdom, a search for truth, or a sense of wanderlust.
For those who now identify with the sign of Ophiuchus, it’s an exciting journey of discovery. Understanding how this newly recognized constellation may influence your life could offer a fresh perspective and insights into your character and destiny.
In this context, a 13-sign horoscope may be worth exploring. It may open up new avenues of understanding, allow for greater specificity, and offer more nuanced insights. Whether you follow the 12-sign or 13-sign system, the key lies in using this knowledge for introspection and personal growth. After all, the stars may guide us, but we shape our destinies.
13-Sign Astrology and Its Implication on Astrology-Based Solutions

The Effect of 13-Sign Astrology on Astrology-based Products and Services
A change as significant as the introduction of Ophiuchus has undeniably influenced the astrology market. Astrology-based products and services, such as horoscope apps, astrology-themed jewelry, and personal chart consultations, have had to adapt to the 13-sign system.
Most noticeably, horoscope and astrology apps now often include options for both 12-sign and 13-sign readings, allowing users to explore and understand their signs under both systems. Similarly, astrological charts and tasks have been adjusted to reflect the shift in sign dates. Jewelry and other astrology-themed products have also expanded, with Ophiuchus often featured prominently as the intriguing new addition.
| Product Type | Impact of 13-Sign Astrology |
|---|---|
| Horoscope and Astrology Apps | Additional options for 13-sign readings |
| Astrology-themed Jewelry | Expansion of product lines to include Ophiuchus |
| Personal Chart Consultations | Adjustments to reflect new sign dates |
Adjusting to the Changes: Advice for Astrology Enthusiasts
In light of these changes, keeping an open mind is essential. For those who’ve discovered they fall under a different sign in the 13-sign system, it can be an opportunity for fresh insights and self-discovery.
Remember, the purpose of astrology is not to dictate but to guide. It provides another lens to view and understand yourself and the world around you. The addition of Ophiuchus doesn’t negate previous knowledge but instead expands it.
Famous Astrological Brands and Their Approach to 13-Sign Astrology
Many renowned astrological brands have recognized the need to adapt and have embraced the 13-sign system. AstroSeek, one of the leading astrology software developers, now offers an option for users to calculate their natal chart based on the 13-sign system. Similarly, Astrology Zone, famed for its detailed monthly horoscopes, provides a comprehensive insight into the 13th zodiac sign, Ophiuchus.
Yet, not all brands have opted to adopt the 13-sign system. Some, like Astrostyle, have continued to follow the traditional 12-sign system, citing its historical significance and the consistency it offers to followers. The approach varies from brand to brand, reflecting the diversity and fluidity of astrology itself.
Regardless of the approach, all these brands have one thing in common: a commitment to providing guidance and insights to their users, whether it’s through a 12-sign or 13-sign lens. As we navigate this new astrological landscape, it’s an exciting time to see how these shifts will further enrich the field of astrology.
Conclusion: Embracing the Uncharted Sky
The introduction of Ophiuchus and the shift to a 13-sign system has undoubtedly left an indelible mark on the field of astrology. It has challenged long-held beliefs and assumptions, inviting us to revisit and revise our understanding of the celestial sphere. The emergence of this ‘new’ sign has broadened the astrological landscape, providing a fresh perspective and a chance for deeper, more nuanced insights.
But what does the future hold for 13-sign astrology? While it’s difficult to predict with certainty, what’s clear is the openness of the astrology community to adapt and evolve. As we venture forward, it’s anticipated that the system will continue to be refined, further incorporating Ophiuchus and potentially bringing about additional changes.
Navigating the new astrological landscape might initially feel overwhelming, especially for those whose sign has changed. The key lies in approaching it with an open mind. Treat this as an opportunity to discover new aspects of yourself and the universe.
Moreover, continue to utilize the myriad of resources available, from astrology apps to personal chart consultations. These tools have adapted to accommodate the 13-sign system and are designed to guide you through this shift.
Change is an integral part of life and is no different in astrology. The addition of Ophiuchus signifies a change, not a loss. It doesn’t render the traditional system obsolete but enriches it by bringing forth a previously uncharted celestial segment.
We encourage you to embrace this change, explore the impact of Ophiuchus on your astrological chart, and delve into the depth it adds to your astrological understanding. By accepting and exploring these changes, we step into a more inclusive and expansive astrological sphere, ever-reflective of our vast and complex universe.

Marta Savova is a journalist, health, technolgy and science writer. With over 20 years of experience in the field, she has published numerous research papers and articles and has a passion for sharing his knowledge with others. He is a regular contributor to several media.

While renewable energy is important for reducing carbon emissions, it’s important to recognize that it alone cannot solve the issue of climate change. There must also be a concerted effort to reduce consumption and promote sustainable lifestyles in developing and developed countries. Focusing solely on renewable energy may distract from the larger systemic changes needed to address climate change.
While partnerships with international organizations and developed countries can benefit developing countries, it’s important to recognize that they can also be exploitative. For example, some international organizations may push for certain renewable energy projects that are not in the best interests of local communities. Developing countries should be cautious when entering partnerships and ensure they have a strong say in decision-making.
The case studies presented in this post are certainly impressive, but it’s important to recognize that not all renewable energy projects are successful. For example, there have been many failed wind energy projects in developing countries due to poor planning and insufficient infrastructure. It’s important to learn from both successes and failures to promote effective renewable energy development.
While renewable energy is certainly promising, it’s worth noting that it may not always be the most cost-effective option for developing countries. For example, some countries may have more abundant and cheaper traditional energy sources, such as coal or natural gas. In these cases, investing heavily in renewable energy may not make sense.
While renewable energy is certainly important for developing countries, it’s worth noting that these technologies can also negatively impact local communities. For example, large-scale hydropower projects can displace indigenous peoples and destroy important ecosystems. It’s important to carefully consider the social and environmental impacts of renewable energy projects before moving forward.
Finally, I disagree with the call to action of sharing this information on social networks. Sharing information is not enough to make a difference. We need to take concrete actions, such as reducing our own consumption, supporting sustainable initiatives, and advocating for policies that protect the environment. Social media is a tool, not a solution in and of itself.
The classification of natural resources into renewable and non-renewable is too simplistic. There are many nuances and complexities to consider, such as the impact of human activity on the environment and the interdependence of different ecosystems. We need a more holistic and integrated approach to natural resource management.
It’s naive to think that conservation and sustainable management will solve all the problems with natural resources. The root cause of the depletion of natural resources is the greed and exploitation of corporations and governments. Unless we address the systemic issues, conservation efforts will only provide a temporary solution.
I also take issue with the idea that minerals are non-renewable resources. While it’s true that some minerals like coal and oil will eventually run out, there are alternatives like renewable energy and recycling that can help reduce our dependence on non-renewable resources. We should focus on investing in these alternatives and finding more sustainable solutions.
I completely disagree with the notion that water is a renewable resource. In many parts of the world, water is already scarce and the situation is only getting worse due to over-extraction, pollution, and climate change. Just because water can be recycled, it doesn’t mean it’s sustainable to use it at the rate we do.